Halogen (compare and contrast between Fluorine and Bromine)
As
we know the element of group 7A produce salts with metals, so they are called
halogen, from a greak word halos- genes, meaning “salt former”. This group contains fluorine
(F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I) and astatine (At). Astatine is
radioactive element. Halogen have 7 valence electrons. Since their atomic
number are less than that of the following noble gases by one, they have -1
oxidation state in their stable compounds. Florine has only -1 oxidation state
in its compounds. Florine is the most electronegative element of the periodic
table. Within this group the electronegativity decreases from fluorine to
iodine. Halogen are the element with the highest electronegativity in each
period, so halogens are the most active nonmetals of each period.
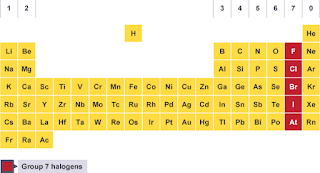
Figure
1. group 7A. halogens
Physical properties
Halogen
are found as diatomic molecules in nature, such as F2, Cl2,
Br2, I2. They are unstable in their monoatomic forms. In the diatomic structure
of the molecules, each atom shares its single electron to achieve a noble gas
electron configuration. Among the halogen, as the atomic number increases, the
melting and biolling points, atomic radius , atomic weight and density also
increase, whereas the ionization energy and non-metallic property decrease from
fluorine to iodine. They are found in nature in the form of halides, except
iodine . it’s found as iodates, such as sodium iodate, NaIO3. At
room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is liquid and iodine
is a solid. Increasing intermolecular force, van der waals force, because of
increasing mass, is responsible for this gradual change from gas to solid.
Chemical properties
As
already mentioned, since the halogens are very active elements, they occure
either as diatomic molecules or in the form of their compound in nature. They
are good oxidizing agents. They have -1 oxidation state in their stable
compound. All halogen, except fluorine (it takes only -1 oxidation), can take
several oxidation number from -1 to +7. Halogen, after the noble gases, have
the second greatest ionization energies. The activity order of halogen is
F>Cl>Br>I. A more active halogen eliminates a less active halogen from
its compounds. That means an active halogen oxidize the other -1 charged halogen
ion into elemental form. We will discuss
about flourine and bromine.
1. Fluorine
The word fluorine is
devided from the latin word “fluere”, meaning flowing. At room temperature,
fluorine is a gas with pale yellow color. It is heavier than air. Since
fluorine has the smallest atomic radius among the halogen, it is the best
oxidizing agent. Fluorine is a very reactive element. It can react vigourously
with a lot of substance at room conditions. It has only -1 oxidation number in
its compounds. Fluorine gas and all fluoride compounds are toxic in large
amounts. But fluoride are essential to life and beneficial in preventing dental
cavities.
In
nature, fluorine is founds as the minerals such as fluorite (CaF2),
kryolite (Na3AlF6) and apatite (Ca5F(PO4)3).
Additionally, fluorine is also found in sea water in trace amounts.
Fluorine
was first discovered by Henry Moissan in 1886 during the electrolysis of KHF2.
Fluorine gas was formed at the anode.
KHF2(l) electrolysis > H2 (g) + F2
(g) + 2KF (l)
9F: 1s22s22p5
Fluorine
oxidizes all elements except He, Ne, and Ar. That means it can react with other
noble gases: Kr, Xe, and Rn.
Xe + 2F2
---------------> XeF4
It is an extremely reactive element. For example, it reacts with hydrogen
explosively, even at -250oC.
H2 + F2
------------------> 2HF
It oxidizes many elements, even in their compounds.
2H2O + 2F2 ------------> 4HF + O2
2HNO3 + 4F2 ---------------------> 2HF + 2NF3 + 3O2
The most
important compound of flourine is hydrofluoric acid, HF. It attacks SiO2
the main constituent of glass, so it can not be stored in glass containers.
HF is used to decorate glassware.
HF molecule
SiO2(s) +
4HF(aq) --------------> SiF4(g) + 2H2O(l)
Na2SiO3(s) + 6HF(aq) ---------->2NaF(aq) + SiF4(g)
+ 3H2O(l)
Ca2SiO3(s) +
6HF(aq) ----------> CaF2(aq) +
SiF4(g) + 3H2O(l)
2.
Bromine
The name
bromine is derived from the latin word “bromos”, meaning “dirty odor”. Bromine
has a dark red color. It is the only liquid nonmental at room temperature. It
is quite dense (3.1 g?cm3) and can be easily vaporized.
Bromine is found in the bodles of some sea creatures and
in sea water. It also exixts as the salts of magnesium and sodium in nature,
but the main source is sea water. Bromine occurs in the sea as bromides. The
concentration of Br- ion in sea water is about 10-3
mol/L.
When
chlorine gas is passed through a solution of salts of bromine, elemental
bromine is obtained.
Bromine is very reactive and toxic. It is a good
oxidizing agent. It can react with a lot of substance at room temperature.
2Al + 3Br2 -----------> 2AlBr3
The
bromide ion, like chloride and iodide, reacts directly with Ag+ and
yields a dirty yellow precipitate.
Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq) ---------------> AgBr(s) (dirty-yellow)
Since
the silver halides, especially silver bromine, are very sensitive to light.
When they are axposed to sunlight, they are aesily reduced to the metallic
silver. As a result of this property, they are used to produse photographic
films.
There
are compare and contrast between fluorine and bromine. Compare is to examine the character or
qualities of especially in order to discover resemblances or differences
or to represent as similar. While contrast is to compare in order to
show unlikeness or differencess, note the opposite natures, purposes, etc.
Character
|
F
|
Br
|
Atomic number
|
9
|
35
|
Configuration of
electrons
|
[He] 2s2 2p5
|
[Ar] 3d10 4s2
4p5
|
The covalent radius (Ao)
|
0,64
|
1,14
|
The radius of X- ion (Ao)
|
1,19
|
1,82
|
Ionation energy level I (kJ/mol)
|
1681
|
1140
|
Electron affinity
|
-328
|
-325
|
Standard reduction
potential, Eo (volt)
|
2,87
|
1,06
|
X-X bonding
energy (kJ/mol)
|
155
|
193
|
H-X bond
energy (kJ/mol)
|
562
|
366
|
Keelektronegatifan
|
4,0
|
2,8
|
Boiling point (oC)
|
-233
|
-7,2
|
Freezing point (oC)
|
-188
|
58,8
|
Beings at25oC
|
Gas (pale
yellow)
|
Liquid (red)
|
Duble bubble maps:
Compare between
fluorine and beomine are halogen. The halogen
group is a highly reactive group that captures electrons (oxidizers). While contrast between fluorine and bromine as
in the table above. At room temperature, fluorine is a
colorless gas or rather yellowish. Bromine
at room temperature is a dark red oil liquid and has a very high vapor
pressure. Liquid bromine is one of the most dangerous general laboratory
reagents, because of its effects on the eyes and nasal passages. Halogen elements can be
identified from the smell and color because it smells stimulating. Fluor is
light yellow and brom
is brown. Being at 25oC, fluor is yellow and brom is
red.

What is the physical properties and chemical properties?
BalasHapusHi nadia. you can see the physical properties of the table above :) there are atomic number, configuration of electrons, etc. And the chemical properties are solubility, reactivity, and oxidation power. Halogen solubility from fluorine to iodine in water decreases, because nonpolar halogen molecules are more soluble in nonpolar solvents. The halogen elements are reactive elements, it is evident that the presence of halogens in nature as compounds. The reactivity of halogens is influenced by their electronegativity. The greater the electronegativity the more reactive the more likely it is to attract electrons. In addition to electronegativity, the reactivity of halogens is also influenced by the halogen bonding energy. The smaller the halogen bonding energy, the easier it is to break the bond so the more reactive the halogen. By looking at the electronegativity data and the halogen binding energy, it can be concluded that the halogen reactivity from top to bottom decreases. At room temperature, fluorine is a colorless gas while bromine at room temperature is a dark red oil liquid and has a very high vapor pressure, and halogens are strong oxidizers. The top-down halogen oxidizing properties are getting weaker, so the halogens can oxidize the halide ions below them.
Hapus
BalasHapusPlease explain to me how the compounds formed from the class of noble gases?
Halogen are found as diatomic molecules in nature, such as F2, Cl2, Br2, I2. They are found in nature in the form of halides, except iodine . it’s found as iodates, such as sodium iodate, NaIO3. At room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is liquid and iodine is a solid. Increasing intermolecular force, van der waals force, because of increasing mass, is responsible for this gradual change from gas to solid.
Hapusmi, can you give me some
BalasHapusexample from mixed?
We can explain mixtures under two titles, homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. We can call homogeneous mixtures as solutions. Coke, sea water, natural gas, Salt water, sugar water, air are examples of homogeneous mixtures. Water+Sand, milk, blood, soil are some common examples of heterogeneous mixtures.
HapusWhat physical properties and chemical properties of a class of noble gases?
BalasHapusyou can see the physical properties of the table above :) there are atomic number, configuration of electrons, etc. And the chemical properties are solubility, reactivity, and oxidation power. Halogen solubility from fluorine to iodine in water decreases, because nonpolar halogen molecules are more soluble in nonpolar solvents. The halogen elements are reactive elements, it is evident that the presence of halogens in nature as compounds. The reactivity of halogens is influenced by their electronegativity. The greater the electronegativity the more reactive the more likely it is to attract electrons. In addition to electronegativity, the reactivity of halogens is also influenced by the halogen bonding energy. The smaller the halogen bonding energy, the easier it is to break the bond so the more reactive the halogen. By looking at the electronegativity data and the halogen binding energy, it can be concluded that the halogen reactivity from top to bottom decreases. At room temperature, fluorine is a colorless gas while bromine at room temperature is a dark red oil liquid and has a very high vapor pressure, and halogens are strong oxidizers. The top-down halogen oxidizing properties are getting weaker, so the halogens can oxidize the halide ions below them.
HapusSo what is the conclusion of the material that you post?
BalasHapuswe know there are compare and contrast between fluor and bromine.
HapusWhat is the basic form to contrast thw element?
BalasHapus"The number of protons" and the number of electrons an element or bond in the nucleus of the atom.
HapusHaii mii... What is the characteristic of halogen??
BalasHapusYou can see the halogen characteristics of the chemical properties and physical properties above
Hapus